HELEN’S TOWN. THE IMPULSE IS TO BEGIN AGAIN

Newton Harrrison,
Research Professor and Director of the Center for the Study of the Force Majeure, the University of California at Santa Cruz, Director of Harrisons Studio, and Professor Emeritus, the University of California at San Diego (CA, USA).
Abstract
Newton Harrison, one of the pioneers and leaders of the eco-art movement, presents his ideas about future eco-urban communities that are self-renewing and occupy a niche in the whole life web. He envisions these communities as centers for the regeneration of herding and farming, made up of groups of around 20,000 people that join together to occupy a new niche in the web of life rather than dominating or using nature. Newton's work reveals the social and cultural activities that need to be developed in order to create such communities, including forestry combined with ecologically knowledgeable herding, the newest forms of agriculture that are polycultural in nature, and an education system that is informed and involved in generating an eco-cultural, empathic community.
Key words: biodiversity, ecopoiesis, autopoiesis, an eco-urban entity, the web of life, the sixth extinction
A planetary trial by fire of our own making is happening
fifty years of our work mostly palliative
community by community city after city sometimes a country
sometimes a bioregion subcontinent even the world ocean
everything we do insufficient I am seeing an inevitable
5 to 6-degree temperature rise with desertification rampant
I am seeing human depopulation
mainly the choice of women but also disease
I am seeing markets disorganized
with deep interruptions in production and distribution
I am seeing a one meter or more ocean rise
with almost a billion people displaced
in these seeings of mine scarcity dominates
human civility and social structures break down
yet also I am seeing new beginnings emerging from the cold northlands
mostly Russia and co-joining countries committing to move through this trial by fire
with their peoples civility ecology intact
I am imagining these countries agreeing to support a system of small towns
expressing what will live well in this near future where the glacial climate
is transformed to arable lands by the increasing heat
and manifest how these communities can live in abundance
I am seeing the birth of this work
as the hiring of a group of botanical scientists
who begin with making Future Gardens
the adolescence of this work is when the Future Gardens mature
telling us what can be farmed what a forest will be like
what herding will be like with increasing heat teaches us
that which will grow and that which will not grow
in these next years of warming
until the future abundance of the life web manifests
in this envisioning Helen’s Towns collectively
become an array of interrelated niches in the emerging life web
of a formerly frozen bioregion
or in small countries like England Switzerland or Sweden
Helen’s Towns can land and readily grow on new fertile ground
even disturbed or glacial earth
never engaging in the destructive processes
of industrial farming herding and forestry
replacing them with new ecosystem abundance models
where the redundancies in the web of life
become the new deep wealth
for all who participate in its regeneration
Introduction
The question that Helen’s Town [1] sets out to answer is whether we can create a complex system, an eco-urban entity, that is self-renewing in nature and includes the whole life web community. We see this particular community as performing the regeneration of herding, farming and small village life of perhaps 20,000 people that all co-join to become a new niche in the web of life. By niche we mean the mutually supporting relational position of a species or population in an ecosystem. Often niches, both large and small, have self-generated boundaries. We begin this work by imagining what, fifty to seventy-five years ahead, in a heat stressed planet, a small community could be like, as it begins again. This arcticle sets out to answer the following question: What are the best practice policies that will permit this generation of small communities to develop, as heat rise in the Siberian Plain attracts refugee populations both from within and external to Russia?
The proposal put forward in this article creates an original synthesis using existing information. Enough historic and scientific knowledge is available, and the urgent need now is to generate solutions at scale where the original research is in the doing. This work reveals the elements that need to be developed in order to collectively express a whole systems synthesis as a working niche[2] in the web of life. The elements include forest (which can become ancient forest in a less than 200-year cycle) combined with ecologically knowledgeable herding, the newest forms of agriculture that are polycultural in nature, and an education system that is informed by and involved in generating an eco-cultural, empathic community. By cultural empathy we refer to the feelings and diverse expressions of identification that peoples from prehistory to the present have developed when attempting to live non-destructively with millions of companion species over extended periods of time. In its simplest form, empathy is a metaphorical state where, for instance, a hunter who kills a deer is in a metaphorical relationship with it; for that moment the hunter is the deer, although not completely. This is a form of empathy with the life taken, expressed through gratitude.
The ecologically based design of this 20,000-person town makes it forageable, carbon positive, and biodiverse. The town can be, and is, processed by the life web during the life of the town and after its use is over. In short, a low-entropy, small town both is possible and much needed. This article provides the key concepts for its initial design. We expect a certain number of these insights will be useful for much larger than village scale communities that may also need to form as a response to extreme warming. By entropy we mean the extraction of resources (energy) from so many planetary life support systems with no equivalent energy restored. Helen’s Town, by its very existence in its own small space, reverses this process.
Background
The present disassociation of western society from both its foundational source, the life web, and from empathy for the life web’s well-being have, in good part, brought about the sixth extinction. We see this state of affairs as a planetary trial by fire, witlessly self-created. This is reflected within industrial processes, overpopulation, wealth accumulation and extreme extraction of resources from most life support systems. The only long-term counter that we think will be effective in this situation is for the majority of the human race that survive the extinctions and heat to find their way to becoming communities that can be local niches within the life web. In this way, the human race can return to behaving like all other species; that is to say, able to play its part in the regeneration of the life web and relinquish its role as destroyer.
At the Center for the Study of the Force Majeure, we believe that there is no longer time to wait for each individual human or group to voluntarily change on the global scale necessary. We consider that the web of life is well on its way to expelling us humans, as it has previously done to other evolutionary mistakes.
We believe that present day capitalism, unless it finds the way to give back to the life web more than it takes, by internalizing biological exchange, will continue to generate this sixth extinction and the overarching simplification and further degeneration of the web of life. The partial collapse of the life web is highly probable, as demonstrated by the physical laws of the conservation of energy. We know that when energy is changed from one form to another there is always a net loss, thermodynamically expressed as entropy.
At present, the global situation appears dire, with the atmospheric commons under stress and producing less oxygen, dropping from 21% to 20%. Moreover, almost 13 million square miles of monocultural farming is in the process of degenerating the life web in the soil. The world forest has been reduced, depending on how the count is made, by between 60 and 70 percent, the world ocean is simplifying itself under extreme stress while human population is increasing in ways that are more than equivalent to ecological resources decreasing. Yet this is only the short list.
Helen’s Town reverses modernist, Cartesian thinking that the world in all its parts is a machine. This is an extremely costly belief that insists on problem solving part-by-part. Helen’s Town sets out to create a complex system that is simultaneously abundant for all participants, that regenerates the life web in all of its operations and that acknowledges interconnectedness as a constant.
We begin with abundance, an ecological concept, which refers to the natural overproduction of species. Most species overproduce in order to survive; whether it be eggs, trees in a forest, ants in an anthill, the examples are more or less equal to the number of species living. Typically, the overproduction of one species is the food for another. For instance, an ancient forest becomes healthier when its overproduction of trees is harvested appropriately. The same is true of farming and for herding. This overproduction or redundancy is the basic wealth of our complex regenerative community. In this context, we see how it is the redundancy that becomes tradeable when excess exceeds local need. In the case of Helen’s Town, we return to source, where the sun is the engine, waste is impossible, and abundance is everywhere. It is in this sense that Helen’s Town is self-making in that it becomes more and more able to continue its existence as it self-complicates, hence, the autopoietic and ecopoetic references.
We came to the conclusion some years ago that the problems we face are now so profound that we must work only on solutions that are systemic and larger than the scale of the issue itself. If not, as fast as we solve problems, the forces of the present marketplace will co-opt (consume) the solutions, causing new problem formations. An example of this is the World Bank’s recent program[3] to buy up most of the commons of developing and poorer nations, proposing the use of technologies that aggressively farm, debase topsoil, and encourage the production of fertilizers to then feed millions as it puts many out of work, while at the same time increasing profit for distant investors.
Conversely, Helen’s Town privileges five of the commons that underlie the wealth of the countryside: the forest, the topsoil, the atmospheric commons, people and the life web itself [4]. This form of eco-urban entity is an expression of preemptive planning, wherein we make a 50 to 75-year environmental prophecy and design backward from it. Our intent is to bring back complexity into our dangerously simplified support systems. To rephrase, the town is designed to be a niche in the life web, literally as well as metaphorically, bringing back agriculture, forestry and herding as meaningful intimate occupations. By meaningful occupation, we refer to activities that are useful to both the individual and to the community, and that trigger positive feedback loops in neural pathways; activities that re-enchant both the participants and their place in the life web. This work is mainly too complex for big machines and much must be done by hand or smaller machines. Thus, we value human labor as essential, as so many highly productive small farms do in our current societies.
Scale and scope
This town for approximately 20,000 people should occupy a space of about 10 km2. The total area for the town with its surrounding land is about 9000 hectares. All structures therein would be made of wood, which functions as a carbon sink. Power would be generated renewably, including for electric transport (maybe even with the return of the trolley). South facing walls (and to a lesser extent the east and west facing walls) are covered with harvestable vines, balconies become orchards carrying two fruit or nut trees on semi-dwarf rootstock. An interlocking park design needs development with the parks and streetscapes also available for foraging. Attention then can be turned to assisting endangered species, considering small game, birds and other pollinators. We trust that the creativity existing in the people who will inhabit this new community will be abundant. We assume here that this creativity, this improvisational power, will be put to work in designing a community town square, main street or both, and the many other micro-civility structures, often electronic in nature, that make for rich cultural activity, along with foraging, as part of everyday life.
We imagine this town conceived in such a way that a person can take a long meander through it, being minimally conscious of urban structure and maximally conscious of the workings of nature, particularly from the perspective of urban foraging. The borders of the town intersect with forest, farm and meadow – all are designed to be productive and biodiverse.
The town that reorganizes the countryside
The proposed town becomes a form that is an understandable shape in the larger countryside, having the potential to become a vibrant form that expresses urban life. The concepts are repeatable, but will differ from place to place, in response to differences in climate, topology, biota and the beliefs of the people who live there. The town teaches other emergent green towns how to become novel ecosystems, developing new niches in the life web.
We propose the land to be owned co-operatively by the town itself and its community. We believe that this kind of living will be attractive to many more than the 20,000 people for which it is designed. If the population is allowed to grow, the commons must grow co-equally. We know from our current models that endless growth is a bad idea, often putting extreme stress on regional ecosystems. So, we argue to impose a limit on houses [5], thus limiting the household presence by the number of kitchens and bathrooms present in the town. This establishes a carrying capacity system that continues through time. The idea here is that over population needs to not exist at all. Living and working in the town becomes a satisfying experience, through working in the farms, herds, forests and maintenance of the novel urban ecosystem operating through the terrain of the town itself.
Helen’s town, the beginning
Assuming that sufficient land can be sequestered, such as public lands, purchased private lands or even contributed lands, the logical beginning would be creating a group of Future Gardens [6]. The working principle of the Future Garden is the idea that highly resilient species and to-be-discovered historical species that lived in the chosen site when it was heat stressed in the past, can be propagated and grown again. The intention is the growing of a body of plants that can live in a three to five-degree (or more) temperature rise. This can be done for grasslands, farming and forestry as a beginning response to an exponentially heat- stressed environment. Ultimately, the Helen’s Town ensemble will give more oxygen than it consumes and sequester far more carbon than it produces: this is its gift both to itself and to the atmospheric commons. From a whole systems perspective, Helen’s Town can be understood as auto poetic, in that it is self-making and emerges from the materials at hand. [7]
Education
Another community gift to the society of the whole is the modest sized teaching system within the town, the core work of which evolves in interlocking parts: the ancient forest, polycultural farming that follows the model of syntropic farming [8], and polycultural herding. Education focuses on enabling biodiversity to inform harvesting in such a way that the system is preserved and can evolve. The education that we have in mind is somewhat influenced by the philosophy of John Dewey as well as Maria Montessori and other educational experimenters that based their systems on learning by doing. The overarching theme is learning by seeing, by doing, environmental feedback and risk taking. The process would be quite different from a conventional university, which functions around students, curriculum and buildings. The teaching here is somewhat parallel to scientific experimentation, tuned to art making. Additional communication takes place through periodic community meetings, where everyone is concerned with the wellbeing of the place as a whole, and the structure of the meeting is similar to that of the Quakers. Although there are many alternative educational platforms in existence, this is unusual in that it is self-invented out of the situation of the place itself. Village life is also enriched and enriching due to its communication with the larger electronic world where it is an active participant. By participant we mean a vastly enlarged electronic presence should exist that tunes this community to others, to educational, political and cultural events planet-wide.
On forestry
Old growth forest can be creatively harvested, maintaining old growth properties that ensure the act of harvesting will preserve the system, by working with a late succession stage before climax. We believe a novel form of forestry could be ecologically, politically and socially accepted, where a wilded 5000-hectare, endangered species forest generates abundance. It is intentionally designed as a mixed conifer and hardwood forest, but with hardwoods dominating. The product of this forest for 150-200 years would be foraging and hunting.
With the passage of years, redwood trees, as an example, would reach 150 feet. Then, one might harvest yearly 1/200th of the 5000-hectare – i.e. a 200-hectare annual harvest spread across 5000-hectare of trees matures, to the point where a hectare may have 140 200-year old trees. Therefore 200-hectare would have 28,000 harvestable trees. While we cannot predict exchange value 150 to 200 years from now, simply multiplying 28,000 trees by $30,000 reveals the present economic value of such a resource. This is calculated on the productivity of a redwood forest, which is far more productive than oak, larch or beech, and this figure would have to be recalculated place by place. The point we make here is that if the majority of future buildings are made from wood, stone and recyclables then environmental benefit is profound; this is especially important in larger urban structures. It is for these reasons that we so highly value forest enterprise and value eco-poetic processes as core to the forest’s long-term survival. However, we continue to focus on the life web’s ability to generate an economy of abundance. Trade value in support of village life is the intention but cannot at present be calculated.
This New Ancient forest is a succession forest, with the succession assisted to speed it up. Species diversity reaches up into and includes top predators – the hawk, the bear, the wolf, the lynx, the wild boar and the human forager as well, although differences place by place can vary greatly according to energies available. This forest also yields fruit, nuts, berries and ground species like mushroom and ground berries like blueberries and blackberries. The forest offers a modest but diverse harvest every year, of wild garlic and onion, while acting as a home for various chains of predation, with the predation niched into the ecosystem, improving species diversity.
On farming
Assuming the farming, herding and foraging will feed this city with considerable left over for trade, how much farmland is needed? If 20,000 people consume three to four pounds of food each per day, that gives a requirement of about 140 million pounds annually. Using syntropic farming, one can expect the system to become increasingly productive after ten years or less. After full maturity we can expect, for example, about 60 tons of food a hectare.
The kind of farming we propose is becoming more widely known and accepted. Syntropic farming, as designed by Ernst Götsch over many years, is now practiced variously around the world. Götsch understands that farming in its present state degenerates topsoil, causes erosion and massive carbon loss, and sets up the conditions for compaction, where the earth will no longer hold water.
From the life web’s perspective, the days of monocultural farming must be over. There are about 12 million square miles of farm land on the planet, somewhat more if topographic folding of lands is calculated. The majority of this farming is influenced by agribusiness technology, which uses artificial fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides and the like. This must cease. Götsch looks to the life web and takes instruction for his farming from succession ecosystems, particularly how each succession over the years enriches the biodiversity of both the soil and companion species. His method of farming does the same thing by tuning profoundly to eco-poetic processes. Thus, over a five to seven-year period, farming can transform itself and within ten years or less be as productive by volume, or more so, than present agribusiness, but with the food produced being more diverse and nutrient dense and the life web respected. Contemporary industrial beliefs in repeatability, scaling up and creating monocultures in farming, forestry and manufacturing need to yield to the dictates of the life web.
On herding
First, we look to generate biodiversity on pastoral lands by retrieving historic methods of herding9. Herds are brought on to fields where there are 30-40 species of grasses and flowers, which is typical of ancient European meadows10. Harvesting by herds happens after the flowers and grasses drop their seeds, thus the act of herding encourages biodiversity. The herd reinforces biodiversity through the act of stamping seeds into the ground and fertilizing the soil, making it organic, nutrient-dense and of the highest quality; medical treatment is also eliminated. Thus, over time, any reduction in productivity in herd animals is far outweighed by the gains: the return of biodiversity and the health gained in the topsoil. In fact, the overall cost of bringing the herd to maturity is significantly reduced. The same applies to companion species - birds, insects, wetlands, small game and a great diversity of plant species.
In temperate environments, a hectare of diverse meadowland can support about one herd animal. So, we propose a 2000-hectare pastureland supporting 2000 creatures, with a two to four-year cycle of culling. This is a humane form, although not the only form of animal husbandry, and provides nutrient dense protein for the community, in combination with a plant-based diet. We believe that from the life web’s perspective, the more we move into a plant-based diet, the more healthy we and the web itself become.
The argument to begin anew is imperative 
Let us imagine that this work and other work of its kind are ignored and not carried out. What then? What if we rigidly continue only making piecemeal improvements in an effort to continue business as usual? This is what appears to be happening currently. If this continues, the 3.5 billion year old life web, in order to adapt to depletion, will continue to simplify its biodiversity, moving toward expelling an apparent evolutionary mistake, human beings. Regenerating itself from extinction may take some 10 to 20 million years; a modest time period when measured against the life web’s long history. If we are absent, who will care?
Helen’s Town, a self-making niche, expressed as a whole systems synthesis, is an eco-poetic offering to the web of life itself. It proposes a modest but compelling act of regeneration, an adaptive response and a path to healing a multitude of particular places on the planet. Helen’s Town is an apology and a gesture of respect to an ecosystem in great need.
In concluding this narrative
I am imagining the Russian Plain and Siberia
looking across the Urals
from Moscow to the North Pole
as one place
And in warming it will become more of one place
And the twenty watersheds that inform this massive region
will clarify what will grow there
I am imagining the Helen’s Towns ensembles
scattered in small number across these watersheds
Informing and being informed by them
setting the stage for a new
bioregional system of interconnected niches
I am talking about a new beginning
in the vast Russian northlands
in this enforced new beginning
we are calling the planetary trial by fire
Sensorium addendum
The Vastlands
A vast new northern landscape becomes visible as a haven for the life web, especially when looking northward from Moscow, past the Urals, into the Siberian Plateau and even into the East Highlands. For instance, the 4 million square kilometer Russian plain joined with the vast Siberian sub plains form a unique body of land, serving a unique grouping of species, endangered and not, within what I call the Vastlands. The creation of a Sensorium for the whole of these lands, although smaller than the world ocean, enables us to view the workings of a complex new future that would ensure the survival of the life web, with human populations functioning as a niche within it. This would secure the continuing of the human race, which at present seems uncertain. We use the term continuing since we consider it important to emphasize the non-static, continuous changing that is inherent in all life forms. The more common word sustainable does not convey the nature of the indeterminacy principle and we consider it misleading. This new envisioning of a Sensorium for this whole region would then produce a survival-based eco-human collaboration. The outcome from this collaboration we envision would be a bi-continental biodiversity continuum. This can then evolve, as species from both Asia and Europe—driven northward by the heat—would then be able to niche into the heat-transformed biota of this vast terrain. At the same time, if syntropic farming, topsoil regenerating and biodiversity technologies are introduced in the food-producing sector of this vast terrain, then finally food production and biodiversity can be in harmony with one another. If this course of action is developed, we would have a bi-continental drought compensatory system at work. Where food is no longer sufficiently produced in drought-ridden Europe and drought-ridden Asia, it can be produced in a re-considered Russian Vastland. We see this effort as of equivalent value to the World Ocean Sensorium. We also see great benefit from creating a scattering of regenerative Helen’s Towns across the Siberian steppes and reaching back into the Russian Plain.
A Vastland Sensorium coupled with Helen’s Town settlements answers a multitude of questions that are scientific in nature and also human and fundamentally ecological as well. The total formation, the concept of human community becoming a self-made niche in a large environment of their own creation, is a profound life web acknowledgement, even an apology, that is collectively eco-poetic in its visualizations as well as autopoietic in its structure.

Where diversity of altitude acts in support of diversity of species, farming, and human cultures
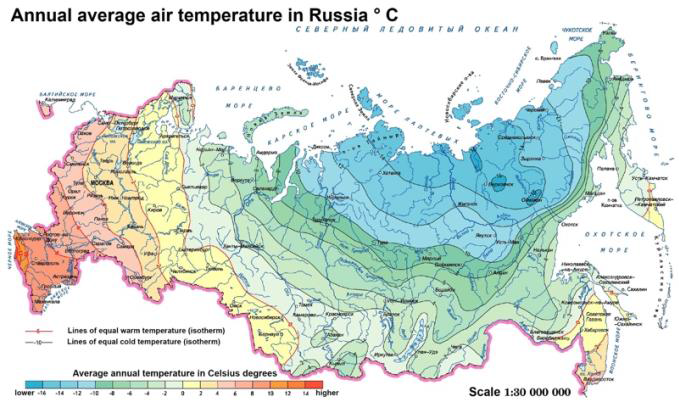
Where the temperature gradients for the whole region move from warm to very cold. This mapping suggests the complexity of change that must be adapted to across the whole region
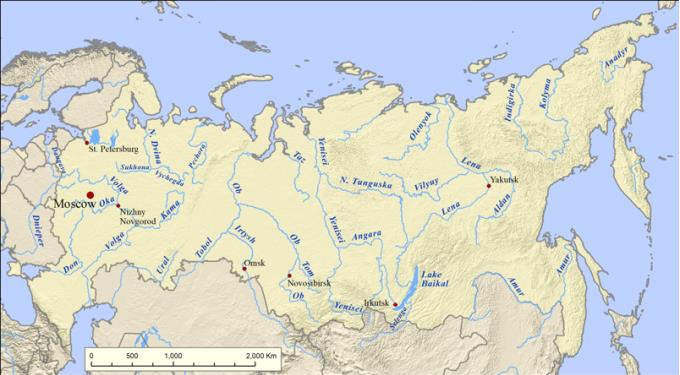
20 watersheds made visible by major rivers. They all shape the lives within them, both similar and different , each watershed adding its own biota and productivity to the whole.
Notes
[1] “Much of the thinking underlying this proposal was done in collaboration with my wife Helen, before she passed. As I wondered how to name the town, I came up with the name of the town as Helen.
[2] I consciously refer to this as a niche in the lifeweb - it is most definitely not the only form of niche for humans in the future. I see the need for humans and their habitat to become a niche in the life web and this is likely the only way in which humans will survive the coming shocks to our planetary systems. These niches, as with all others in the life web, will take many forms, developed, defined and refined in relation to all other factors – place, participants, other biodiversity. I invite any and all creative suggestions for other ways of re-harmonizing our human lives with the life web, and I share Helen’s Town as one possible way.
[3] https://www.oaklandinstitute.org/highest-bidder-takes-all-world-banks-scheme-privatize- commons?fbclid=IwAR2nKhjb9Tml_ZuH7CS4NMziK0RQGMeIfdQIsD4XTxjmrsTMzCHuOIQp-X
[4] Unexpectedly, we suddenly saw the life web itself as a commons, and understood its inclusion here to be a useful illustration of the nested thinking inherent in this work.
[5] The life web has, over the ages, invented systems that are self-limiting, with an ecotone, or a boundary that locates their limitation in relationship to other systems, which may indeed feed on each other, but nonetheless, the boundary limitations are what let them continue. Our suggestion that no more houses be built or kitchens (produced food consumed) made or bathrooms (waste produced and processed) made, is our way of generating population limitation. Therefore, rather than expanding population and stressing a good working system, we argue that a new system be generated to handle population increases if they continue.
[6] http://www.centerforforcemajeure.org/future-gardens
[7] See Santiago Theory. A foundational aspect of Helen’s Town’s ability to grow and evolve is that it’s eco system is eco-poetic—that is, self-making, self-growing, and self-serving.
[8] Ernst Götsch, lifeinsyntropy.org and agendagotsch.com
Reference for citations
Harrison, N. (2021). Helen’s Town. The impulse is to begin again. Ecopoiesis: Eco-Human Theory and Practice, 2(2). [open access internet journal]. – URL: http://en.ecopoiesis.ru (d/m/y)
